Kickstart your financial analysis and investing career by understanding the ratios and numbers that make a great company.
Reading financial statements is a critical skill for any investor. These reports provide important information about a company’s financial health, performance, and prospects.
The three main types of financial statements are the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. Each one provides a different perspective on a company’s finances.
How to Read Financial Statements
What are financial statements?
A financial statement is a formal document that discloses a company’s financial position and performance. Financial statements include a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Why are financial statements important?
Financial statements are important because they provide a snapshot of a company’s financial position and performance. They help investors, lenders, and other stakeholders assess a company’s overall health and make informed decisions about investing in it. Financial statements are also used to calculate a company’s credit score, which is important for obtaining loans and other financing.
How to read financial statements
Reading financial statements can be tricky, but with a little practice, you’ll glean a lot of important information from them. Here are some tips for reading financial statements:
- Start by looking at the balance sheet. This will give you a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Look at the income statement. This will show a company’s revenue, expenses, and net income.
- Finally, take a look at the cash flow statement. This will show you a company’s inflows and outflows of cash.
- Once you’ve reviewed all three financial statements, you’ll understand a company’s financial position and performance well.
The Easiest Way to Read Financial Statements
The easy way to read financial statements is by harnessing the power of modern investing tools like Stock Rover. Dive in, filter out noise, and discover gems that align with your investment goals. Stay sharp with real-time reports that flag potential pitfalls automatically.
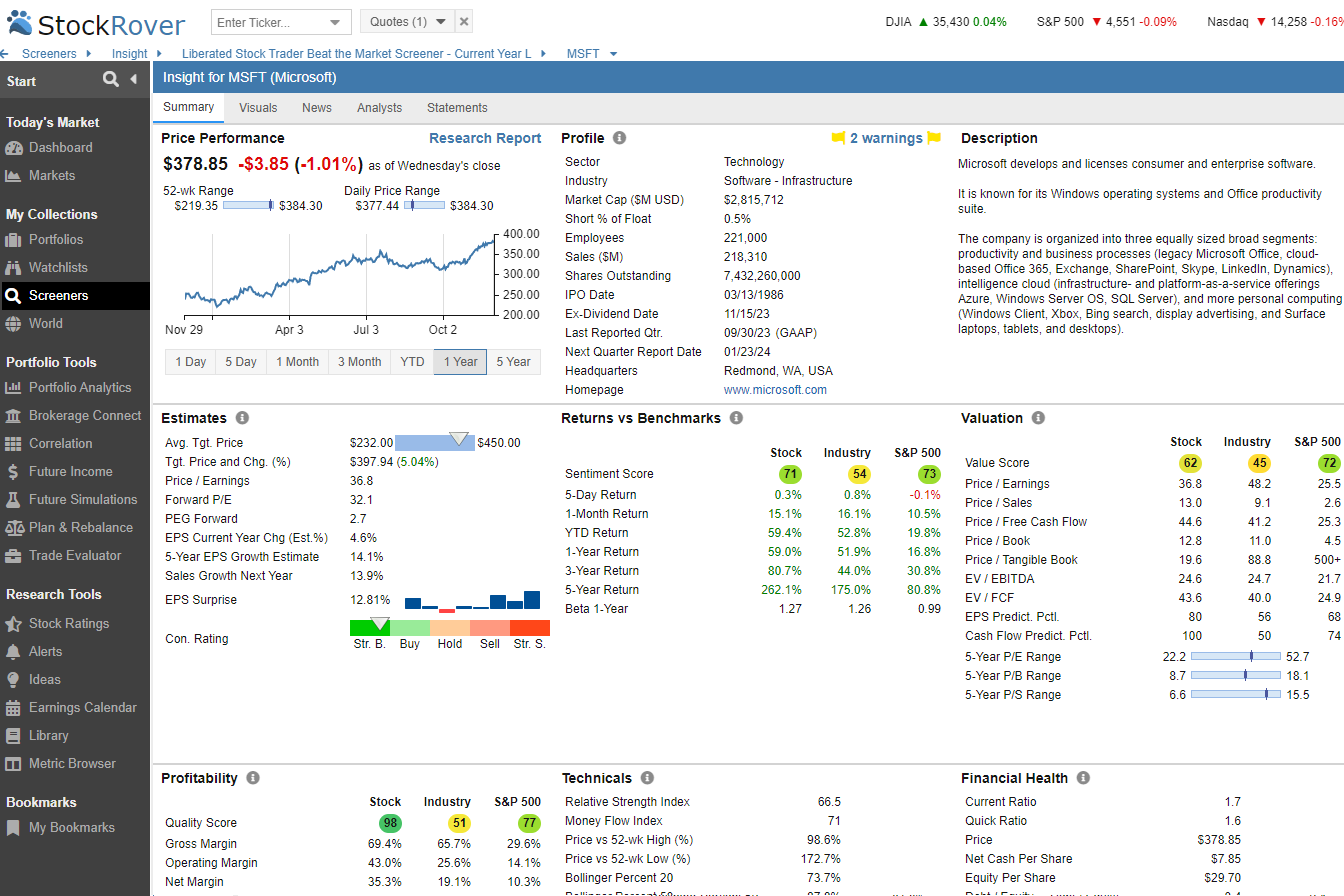
Try Powerful Financial Analysis & Research with Stock Rover
What are the four financial statements?
The four financial statements are the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and statement of shareholders’ equity.
- The balance sheet shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- The income statement shows a company’s revenue, expenses, and net income.
- The cash flow statement shows a company’s inflows and outflows of cash.
- The statement of shareholders’ equity shows a company’s changes in equity over time.
1. The Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets are resources that the company owns or controls, such as cash, inventory, property, and equipment. Liabilities are debts or obligations the company owes to others, such as loans or accounts payable. Equity represents the owners’ claims on the company’s assets.
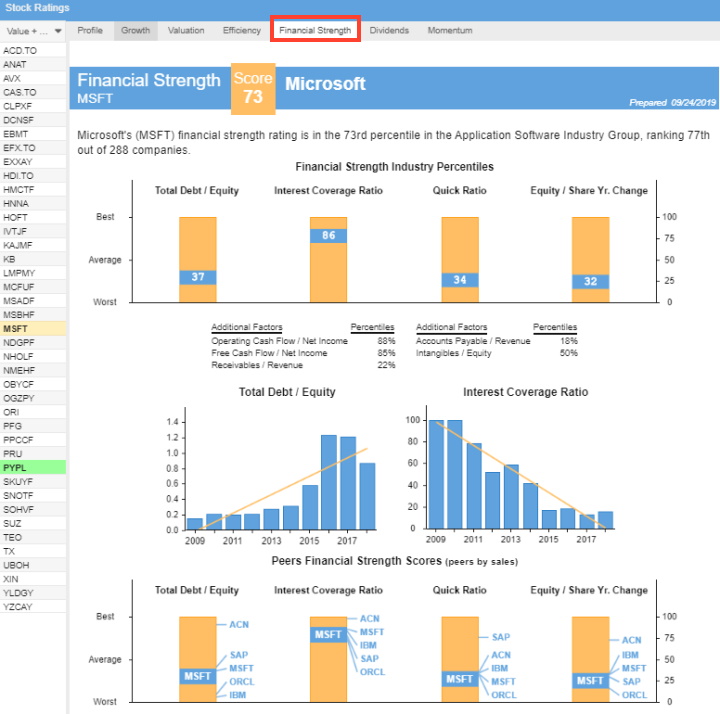
The balance sheet follows the basic accounting equation: assets = liabilities + equity. This means that for every dollar in assets, there must be an equal amount in liabilities and equity. The balance sheet is important because it provides investors with information about a company’s financial health and ability to meet its short-term and long-term obligations.
2. Income Statement
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, shows a company’s revenue and expenses over a specific period. Revenue is the money that a company earns from selling its products or services, while expenses are the costs incurred in running the business.
The bottom line of an income statement shows whether a company made a profit or suffered a loss during the specified period.
3. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the flow of cash into and out of a company over a specific period of time. It provides information about where the cash is coming from (cash inflows) and how it is used (cash outflows). This helps investors understand how well a company manages its cash and if it has enough liquidity to cover its expenses and investments.
The cash flow statement is divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Operating activities include the cash flows from a company’s primary operations, such as sales of products or services. Investing activities include cash flows from buying or selling assets, such as property or equipment. Financing activities involve borrowing money (cash inflow) or repaying debt (cash outflow), as well as issuing stock (cash inflow) or paying dividends (cash outflow).
4. Statement of Shareholders’ Equity
The statement of shareholders’ equity is a financial statement that shows the changes in a company’s stockholders’ equity over a period of time. Stockholders’ equity, also known as shareholders’ equity or simply “equity,” is the amount of money that would be returned to shareholders if all of the company’s assets were liquidated and all its debts were paid off.
This statement begins with the balance of retained earnings, the accumulated profits reinvested into the company instead of being distributed to shareholders as dividends. It then shows any changes in this balance due to net income or loss, dividends paid out, and any adjustments for accounting errors or changes in accounting principles.
My thorough testing awarded TradingView a stellar 4.8 stars!
With powerful stock chart analysis, pattern recognition, screening, backtesting, and a 20+ million user community, it’s a game-changer for traders.
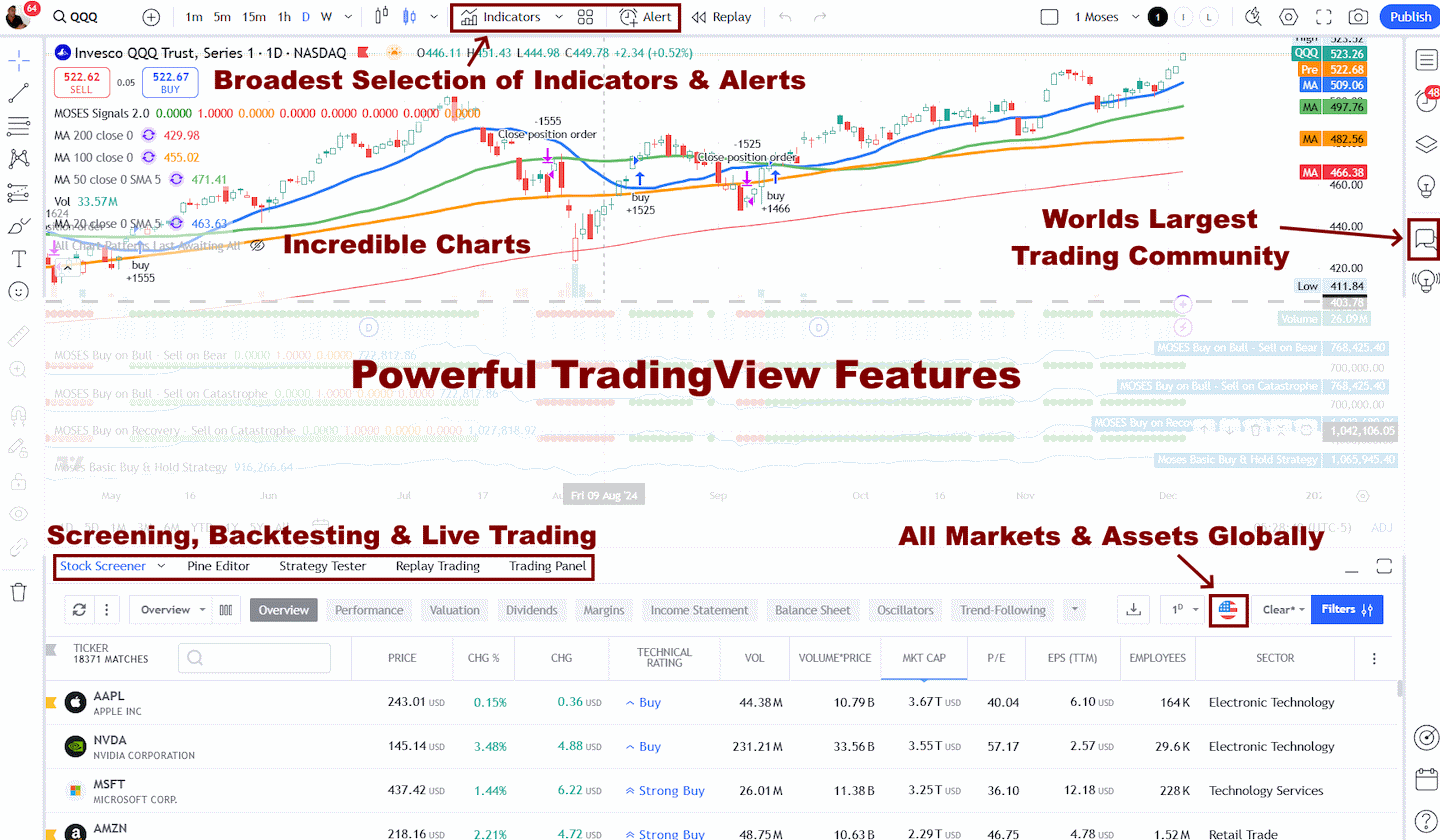
Whether you're trading in the US or internationally, TradingView is my top pick for its unmatched features and ease of use.
Explore TradingView – Your Gateway to Smarter Trading!
8 red flags to look for in financial statements
Red flags to look for when reading financial statements include if a company’s liabilities exceed its assets, if expenses exceed revenue, if cash flow is negative, or if the debt-to-equity ratio is too high.
- Inconsistent or Unusual Changes in Key Numbers: One of the first things to look for when analyzing financial statements is any sudden or unexpected changes in key numbers, such as revenue, expenses, and net income. This could indicate potential issues with the company’s operations or financial health.
- High Levels of Debt: A high debt-to-equity ratio can signal that a company may be overleveraged and at risk of defaulting on its obligations. It is important to compare a company’s debt levels to those of its competitors and industry standards.
- Lack of Cash Flow: Cash flow is a crucial indicator of a company’s financial strength, as it represents the cash coming in and going out over a period of time. A negative cash flow could mean the company struggles to generate enough revenue to cover expenses.
- Inconsistent Earnings: Fluctuations in a company’s earnings can be a red flag, as it may indicate instability in the business or potential accounting manipulation. It is important to look at trends over time rather than focusing on just one period.
- Changes in Management: A sudden change in key management positions, such as the CEO or CFO, could signal internal issues within the company. Researching the reasons for the change and how it may impact the company’s operations and financials is important.
- Legal Troubles: Legal troubles such as lawsuits, regulatory investigations, or fines can greatly impact a company’s financial health and reputation. It is important to look into the details of any legal issues and how they may affect the company’s operations and financials.
- High Debt Levels: Companies with high debt levels may struggle to meet their financial obligations, especially during economic downturns. Analyzing a company’s debt-to-equity ratio and comparing it to industry averages is important.
- Insider Trading: When insiders, such as top executives or board members, buy or sell stock in their own company, it can signal their confidence in the company’s future performance. However, a sudden increase in insider selling or buying activity could also indicate potential problems within the company.
Try TradingView, Our Recommended Tool for International Traders
Global Community, Charts, Screening, Analysis & Broker Integration
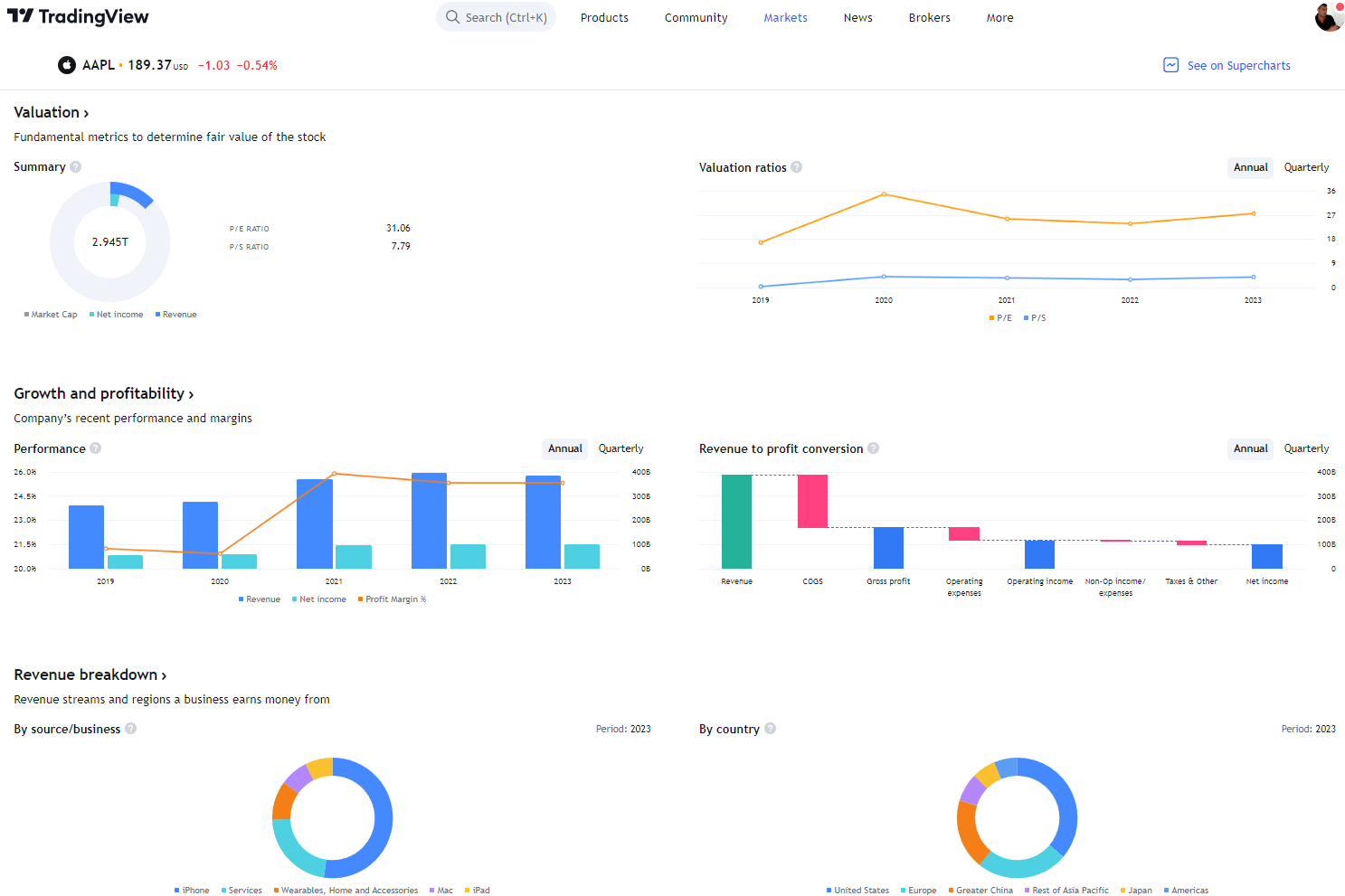
Global Financial Analysis for Free on TradingView
How are the financial statements linked?
The four financial statements are linked because they show a company’s financial position and performance over time.
The balance sheet shows a company’s assets and liabilities at a specific time, the income statement shows how those assets and liabilities have changed, and the cash flow statement shows how the company’s cash flow has changed over time.
These three statements give a complete picture of a company’s financial health. The statement of shareholders’ equity shows how the value of a company’s shares has changed over time.
What are consolidated financial statements?
Consolidated financial statements are financial statements that include the financial results of a parent company and its subsidiaries. When a parent company owns a majority stake in a subsidiary, the two companies are considered to be consolidated. Consolidated financial statements provide a complete picture of a company’s financial position and performance. They can be used to assess the overall health of a company and its subsidiaries and make informed investment decisions.
How are financial statements used in decision-making?
Financial statements are often used in decision-making. They can help investors, lenders, and other stakeholders assess a company’s overall health and make informed decisions about investing in the company. Financial statements are also used to
What are interim financial statements?
Interim financial statements are financial statements that are not prepared on a company’s annual basis. They are generally compiled every three or six months and can be used to track a company’s progress over time and make informed decisions about its future. Interim financial statements can assess a company’s liquidity, solvency, and profitability. They can also be used to compare companies in the same industry.
Where can you find short-term investments on financial statements?
Short-term investments can be found on a company’s balance sheet. They are listed under the category of “current assets.” Short-term investments are generally considered less risky than long-term investments and can be used to generate income or finance short-term needs.
Which financial statements show depreciation expense?
The income statement and cash flow statement show depreciation expenses. The depreciation expense is listed under the category of “expenses.” It is important to note that depreciation is a non-cash expense that does not affect a company’s cash flow. Depreciation is used to match the cost of an asset with the revenue that it generates.
What are management’s responsibilities regarding financial statements?
Management is responsible for preparing and presenting financial statements that are accurate and informative. Financial statements must be prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Management is also responsible for ensuring that the company’s financial statements are free of material misstatements.
Where to find inventory on financial statements?
Inventory is listed under the category of “current assets” on a company’s balance sheet. It represents the goods a company has on hand and available for sale. It is important to note that inventory can be subject to depreciation and other valuation adjustments.

