Stock futures are derivative contracts that track the future price of a certain stock.
They are agreements to buy or sell a specific stock at a predetermined price on a future date.
Stock futures allow investors and traders to speculate on stocks without purchasing them.

What Are Stock Futures?
A stock future is a contract between two parties to buy or sell shares of a particular stock at a predetermined price on a specified date in the future. The contract is standardized so that it can be traded on an exchange.
The contract’s price is determined by the value of the underlying stock, with the contract issuer agreeing to pay the difference between the agreed-upon price and the actual price of the shares when the contract expires.
The party who agrees to buy the stock in the future is said to be “long,” while the party who agrees to sell the stock in the future is said to be “short.”
What are futures contracts?
Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an underlying asset at a future date at a price that is agreed upon today. Investors often use futures contracts to speculate on the direction of a given asset’s price or to hedge against potential price swings.
What are stock index futures?
Index futures are financial instruments based on stock index values, reflecting the underlying stocks’ price and market capitalization. Unlike other futures contracts, index futures are settled in cash, eliminating the need for physical delivery. These contracts are often acquired to construct diversified portfolios and effectively manage the risk of market downturns.
My thorough testing awarded TradingView a stellar 4.8 stars!
With powerful stock chart analysis, pattern recognition, screening, backtesting, and a 20+ million user community, it’s a game-changer for traders.
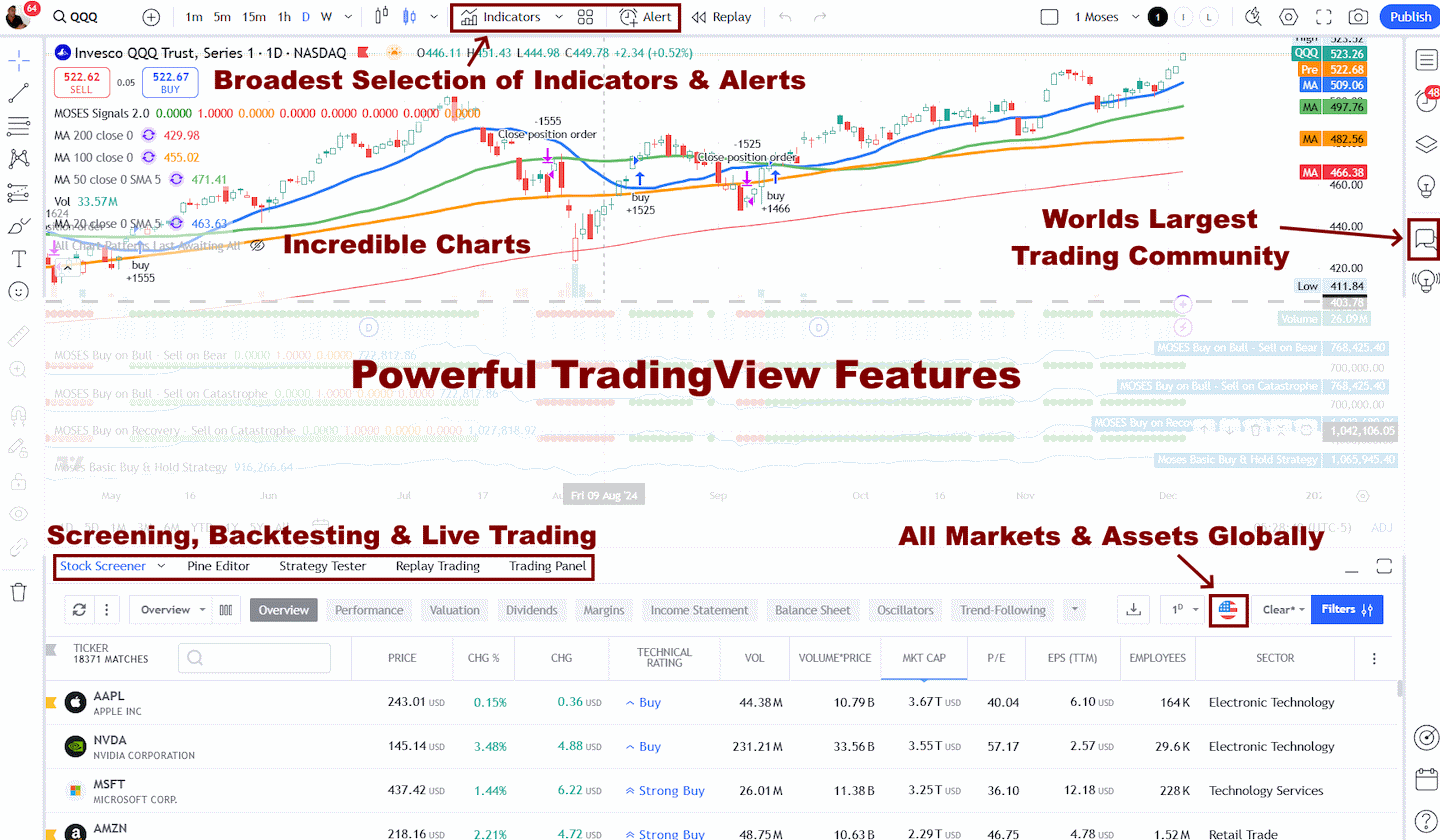
Whether you're trading in the US or internationally, TradingView is my top pick for its unmatched features and ease of use.
Explore TradingView – Your Gateway to Smarter Trading!
1. S&P 500 Futures
The S&P 500 Futures is a type of stock futures contract based on the value of the S&P 500 Index. The S&P 500 Index is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 large, publicly traded companies. The S&P 500 Futures is traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
See this Futures Chart Live on TradingView
2. E-mini S&P 500 Futures
An E-mini S&P 500 Future is a stock futures contract based on the value of the S&P 500 Index. It is smaller than a regular S&P 500 Futures contract, which makes it easier for new investors to get started. The E-mini S&P 500 Futures are traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
Trade this Futures Chart Live on TradingView
3. Dow Jones Industrial Average Futures
The Dow Jones Industrial Average Futures is a type of stock futures contract based on the value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), a stock market index that tracks the performance of 30 large, publicly traded companies. The Dow Jones Industrial Average Futures are traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
Financials & Futures Charts Live on TradingView
4. Nasdaq Composite Index Futures
The Nasdaq Composite Index (COMP) is a stock index that tracks the performance of more than 3,000 large, publicly-owned companies listed on the Nasdaq Stock Exchange. The Nasdaq Composite Index is a stock market index that tracks the performance of over 3,000 companies listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market. The Nasdaq Composite Index Futures are traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
The Best Charts Live on TradingView
5. Nasdaq 100 Futures
The Nasdaq 100 Index (NDX) is a stock index that tracks the performance of 100 large, publicly-owned companies listed on the Nasdaq Stock Exchange. The NDX is often used as a benchmark to measure the overall performance of the US technology sector.
See this Futures Chart Live on TradingView
6. Russell 2000 Futures
The Russell 2000 Index (RUT) is a stock index that tracks the performance of 2,000 small, publicly-owned companies in the United States. The RUT is often used as a benchmark to measure the overall performance of the US stock market.
A Global Trading Community on TradingView
How do stock index futures work?
When you buy a stock index future, you agree to buy or sell shares of the underlying stock index at a predetermined price on a specified date. The contract is standardized so that it can be traded on an exchange. The price of the contract is determined by the price of the underlying stock index, with the contract issuer agreeing to pay the difference between the agreed-upon price and the actual price of the shares when the contract expires.
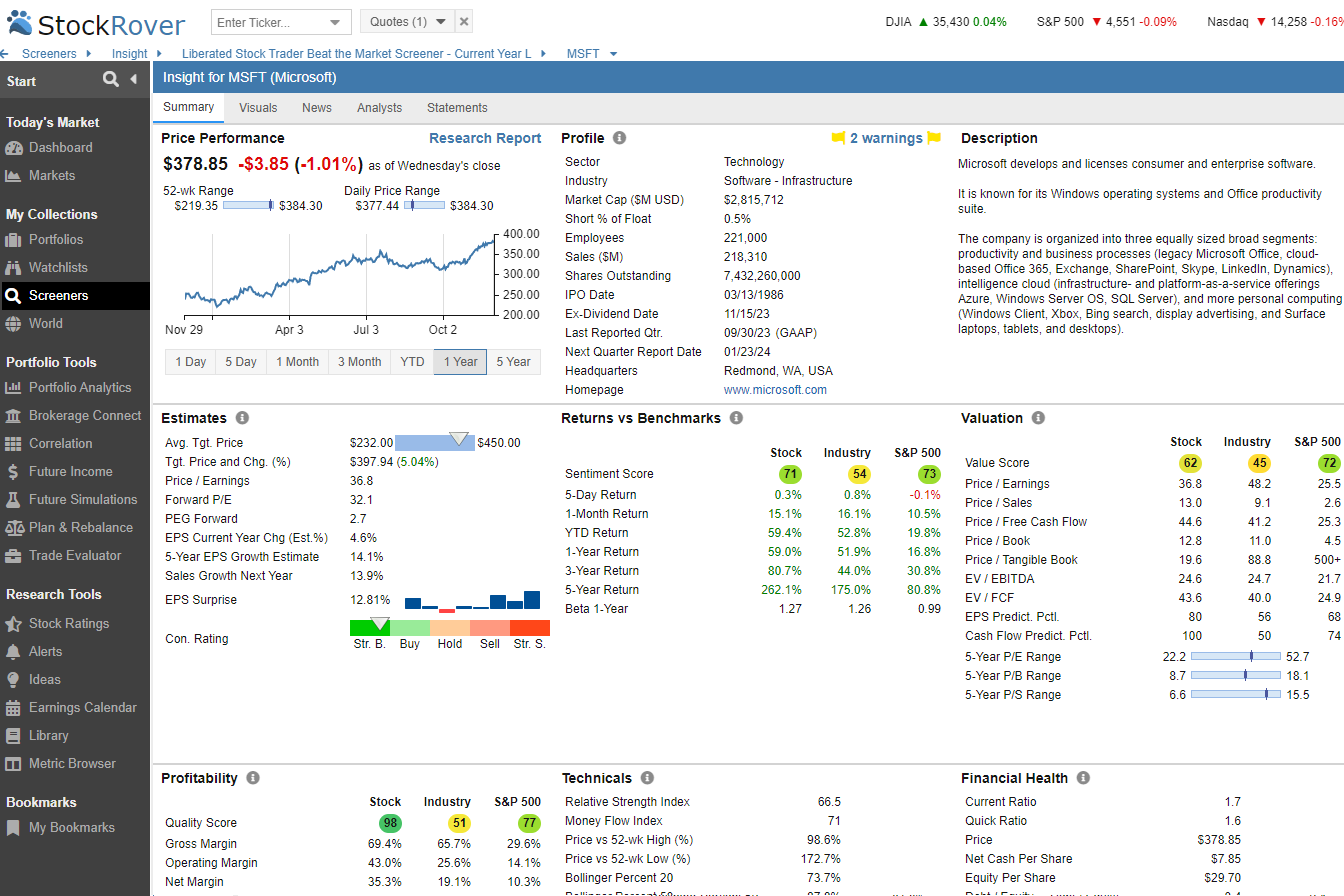
Try Powerful Financial Analysis & Research with Stock Rover
How do stock futures work?
When you buy a stock future, you bet the underlying stock’s price will increase. Conversely, when you sell a stock future, you bet the underlying stock’s price will go down.
Stock futures are traded on exchanges and have standard contract sizes, tick values, and expiration dates. The most popular stock futures contracts are for shares of large companies such as Apple, Google, and Amazon.
The price of a stock future is not always equal to the price of the underlying share, but it is usually very close. This is because stock futures are “marked to market” daily. This means that if the price of the underlying shares goes up or down, the corresponding futures contract will also go up or down by a similar amount.
You want to be a successful stock investor but don’t know where to start.
Learning stock market investing on your own can be overwhelming. There’s so much information out there, and it’s hard to know what’s true and what’s not.
Liberated Stock Trader Pro Investing Course
Our pro investing classes are the perfect way to learn stock investing. You will learn everything you need to know about financial analysis, charts, stock screening, and portfolio building so you can start building wealth today.
★ 16 Hours of Video Lessons + eBook ★
★ Complete Financial Analysis Lessons ★
★ 6 Proven Investing Strategies ★
★ Professional Grade Stock Chart Analysis Classes ★
Do futures predict stock market prices?
One common misconception about stock futures is that they can be used to predict where the stock market is headed. While it’s true that they can be used to hedge against downside risk or speculate on future movements in individual stocks or the broader market, it’s important to remember that stock futures are not an accurate predictor of where the stock market is headed.
Do stock futures predict prices for the next day?
There is no clear answer to whether or not stock futures predict prices for the next day. Some investors believe they can be used to predict future stock prices, while others believe they are only effective at hedging against downside risk. However, there is no definitive evidence that proves either side is correct.
Buying stock index futures
To buy a stock index future, you must first open a futures account with a broker. Once you have an account, you can place an order to buy a contract on the desired stock index. The price of the contract is determined by the price of the underlying stock index, with the contract issuer agreeing to pay the difference between the agreed-upon price and the actual price of the shares when the contract expires.
Stock futures offer several benefits for investors, including:
- The ability to speculate on the direction of a given stock’s price
- The ability to hedge against potential price swings
- The ability to trade on a margin
- The ability to trade 24 hours a day during the workweek
The risks of trading stock futures include market volatility, liquidity, interest rate, and counterparty risks. Market volatility refers to the fluctuations in the price of a security or index. Liquidity risk is the risk that a security or index may not be able to be sold at its current price due to a lack of buyers. Interest rate risk is the risk that changes in interest rates will impact the value of a security or index.
Like all investments, there are risks associated with trading stock futures. These risks include:
- The potential for loss
- The potential for volatile prices
- The potential for margin calls
- The potential for slippage
- The potential for counterparty risk
Before trading stock futures, be sure to understand the risks involved and learn about strategies that can help mitigate these risks.
Investing In Stocks Can Be Complicated, Stock Rover Makes It Easy.
Stock Rover is our #1 rated stock investing tool for:
★ Growth Investing - With industry Leading Research Reports ★
★ Value Investing - Find Value Stocks Using Warren Buffett's Strategies ★
★ Income Investing - Harvest Safe Regular Dividends from Stocks ★

"I have been researching and investing in stocks for 20 years! I now manage all my stock investments using Stock Rover." Barry D. Moore - Founder: LiberatedStockTrader.com
Are stock futures accurate?
Stock futures are not guaranteed to be accurate, based on predictions, and not guaranteed to reflect actual future performance. However, many institutional investors find them useful tools for planning and decision-making.
Are futures the same as stocks?
No, futures are not the same as stocks. A stock is a share of ownership in a company, while a futures contract is an agreement to buy or sell a particular stock at a predetermined price on a specified date in the future.
Where are stock futures traded?
Stock futures are traded on exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and are used by institutional investors to speculate on the stock market’s future direction. Hedgers can also use them to protect against downside risk in the stock market. For example, if you owned shares of ABC Company and were worried about a drop in the stock price, you could buy a put option on ABC Company’s stock. If the stock price did indeed drop, you would offset some of your losses with the gains from your put option.
Lot Size in the Futures Market
The futures market functions through contracts that specify a standardized quantity of the financial instrument or derivative security to be delivered.
The lot size of these contracts can vary based on the commodity or instrument being traded. Trading futures on margin enables traders to take larger positions than their capital allows. Exchanges establish standard lot sizes to promote market transparency and efficiency.
How Are Stock Futures Calculated?
Stock futures prices are determined by supply and demand in the marketplace. The price increases when more people want to buy a particular futures contract than sell it, and it decreases when more people want to sell a particular contract than buy one.
The most important factor in determining the price of stock futures is often said to be the”fundamental value” of those shares in the days ahead, but many other factors can also affect those trading values, including trader psychology and changes in the political landscape.
What is the formula to calculate stock index futures?
The formula to calculate stock index futures is:
F = S x (P – PE) / (Q x V)
Where:
- F = Futures price
- S = Spot price
- P = Price of the underlying asset
- PE = price of the underlying asset at expiration
- Q = Quantity of the underlying asset
- V = value of the contract
The relationship between stock index futures and stock prices
Stock index futures and stock prices reflect the same underlying market conditions. When the price of a stock goes up, the value of its index future is affected. Similarly, when the price of a stock goes down, it can also affect its index future. This is because traders use futures contracts to speculate on where the overall stock market will be at a certain point in the future, and by doing so, they indirectly affect the prices of stocks.
Stock index futures and stock prices are determined by market supply and demand. However, stock index futures are also affected by the “fundamental value” of the underlying shares. This means that stock index futures can predict future movements in the stock market, while stock prices are only affected by current supply and demand.
Sometimes, those prices might seem irrational, but they almost always follow suit with what is happening in the marketplace on a given day.
When do stock futures open?
Stock futures traded on CME Globex typically open at 6:00 p.m. EST Sunday and close at Friday 5:00 p.m. EST, with a daily settlement period break from 5:00 p.m. to 6:00 p.m.
There are some exceptions. For example, options on stock index futures typically have longer trading hours than regular stock futures.
Stock futures traded on CME ClearPort typically open at 6:00 p.m. EST Sunday and close at 6:45 p.m. EST Friday, with a daily settlement period break from 6:45 p.m. to 7:00 p.m. EST Monday through Thursday.
Check the CME Group website for opening and closing times. S&P Mini contract details.
When do stock futures open on Sunday?
Stock futures traded on CME Globex and CME ClearPort typically open at 6:00 p.m. EST Sunday.
What time do stock futures open?
Stock index futures contract opens daily from Sunday to Friday at 6 p.m. EST or 5 p.m. CT.
How do I see stock futures?
The best place to view stock and index futures is on TradingView. Its interactive charting, screening, financials, and global trading community are world-class.
Alternatively, you can visit the CME Group website. Once on the website, select “Products and Services” from the toolbar at the top of the screen and then select “Futures.” This will take you to a page where you can view all the stock futures contracts traded on CME Globex.
Ever Dreamed of Beating the Stock Market
Most people think that they can't beat the market, and stock picking is a game only Wall Street insiders can win. This simply isn't true. With the right strategy, anyone can beat the market.
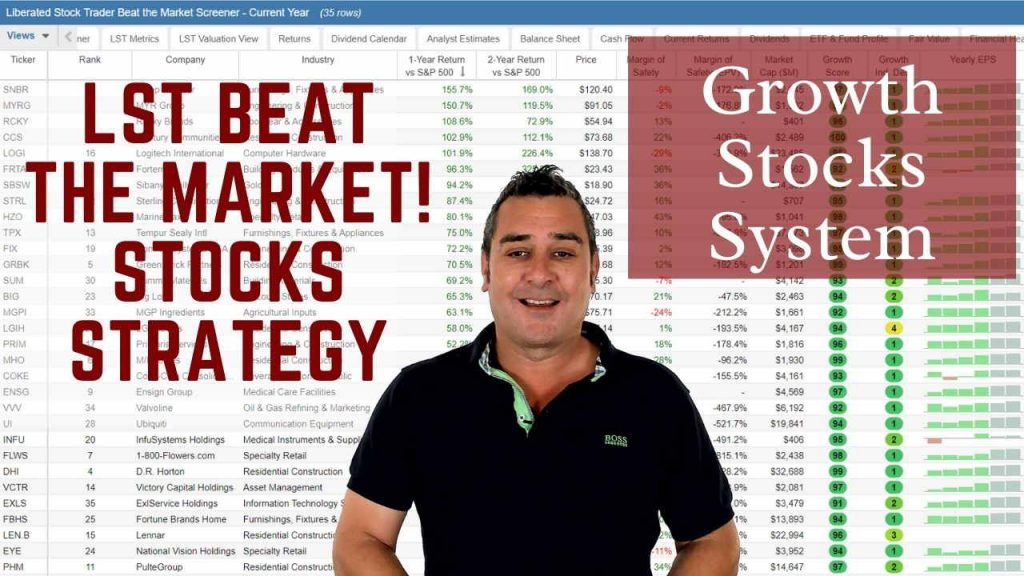
The LST Beat the Market Growth Stock Strategy is a proven system that has outperformed the S&P500 in 8 of the last 9 years. We provide all of the research and data needed to make informed decisions, so you no longer have to spend hours trying to find good stocks yourself.
The LST Beat the Market System Selects 35 Growth Stocks and Averages a 25.6% Annual Return
★ 35 Stocks That Already Beat The Market ★
★ Buy The Stocks & Hold For 12 Months - Then Rotate ★
★ Fully Documented Performance Track Record ★
★ Full Strategy Videos & eBook ★
Take The Pain Out Of Stock Selection With a Proven Strategy
Conclusion
Stock futures are a type of financial contract that allows investors to speculate on future movements in individual stocks or broader markets.
Hedgers can also use them to protect against downside risk in these markets.
Despite their usefulness, it’s important to remember that stock futures should not be used to accurately predict where markets are headed due largely to their complex calculation process, which factors in many elements beyond pure market data analysis.
FAQ
What is the best platform for trading stock futures?
TradingView is widely considered to be the best platform for trading stock futures. It offers extensive research tools, powerful charting capabilities, and access to real-time global exchange data. Additionally, TradingView has a large community of traders who share their ideas in public chatrooms.
What are stock futures?
Stock futures are financial contracts that oblige the buyer to purchase and the seller to sell a specific quantity of an underlying stock at a predetermined price on a set future date. They're a derivative product used for hedging and speculation.
How do stock futures work?
Investors buy and sell futures contracts before the expiry date. The difference between the buying and selling price determines their gain or loss. The transactions are facilitated through a futures exchange.
What is a futures exchange?
A futures exchange is a marketplace where futures contracts are traded. It ensures fair trading practices and protects investors through regulations and oversight.
What's the purpose of stock futures?
Stock futures allow investors to hedge against price fluctuations, lock in prices for future transactions, and speculate on price movements for potential profit.
Why are futures prices different from spot prices?
Futures prices incorporate time value, interest rates, and expected dividends, making them different from spot (current market) prices.
What are long and short positions in futures?
Taking a long position means buying a futures contract anticipating the stock's price will rise. A short position involves selling a futures contract, expecting the price to decline.
What is the margin in futures trading?
Margin is the money a trader must deposit to open or maintain a futures position. It's an insurance policy that protects the broker from losses and helps traders manage risk. Margin requirements vary by instrument and can change frequently due to market volatility.
What are the risks associated with futures trading?
Futures trading involves the risk of loss and can be extremely volatile. Risks include volatility of prices, liquidity risk, risk of forced liquidation due to margin calls, counterparty risk, and systemic market risk. As such, managing positions correctly and having an appropriate trading plan is important.
What is mark-to-market in futures trading?
Mark-to-market involves adjusting the value of a futures contract at the end of each trading day to reflect its current market price.
What happens at the expiration of a futures contract?
At expiration, futures contracts are either settled by physical delivery of the underlying asset or with stock futures a cash settlement, depending on the contract terms.
Can individual investors trade futures?
Yes, individual retail investors can trade futures, but it requires a thorough understanding of the market and sufficient capital and risk tolerance.
How do I start trading futures?
To trade futures, you must open a brokerage account that supports futures trading, deposit the required margin, and familiarize yourself with futures trading platforms. I recommend TradingView as it integrates with major futures brokers at preferential rates.
What is a stock futures contract size?
Stock futures contracts typically have a value of 100 shares per contract. For example, if the price of a stock is $150, each contract will be worth $15,000 (100 x $150). You can also trade fractional contracts, such as 10 or 50-share contracts in some cases. Before trading futures, make sure to understand all contract details and fees.
How to Trade Futures Using Commitment of Traders (COT) Report

